OPEN-SOURCE SCRIPT
Atualizado Anchored Geometric Brownian Motion Projections w/EV
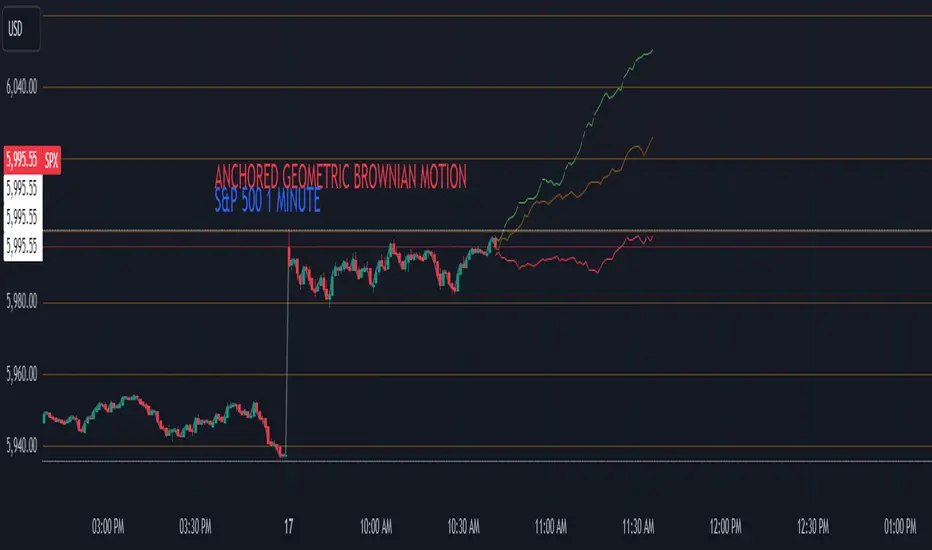
Anchored GBM (Geometric Brownian Motion) Projections + EV & Confidence Bands
Version: Pine Script v6
Overlay: Yes
Author: [Gary Sebastian Brown III]
Published On: [12-31-24]
Overview
The Anchored GBM Projections + EV & Confidence Bands indicator leverages the Geometric Brownian Motion (GBM) model to project future price movements based on historical data. By simulating multiple potential future price paths, it provides traders with insights into possible price trajectories, their expected values, and confidence intervals. Additionally, it offers a "Mean of EV" (EV of EV) line, representing the running average of expected values across the projection period.
Key Features
Anchor Time Setup:
Define a specific point in time from which the projections commence.
By default, it uses the current bar's timestamp but can be customized.
Projection Parameters:
Projection Candles (Bars): Determines the number of future bars (time periods) to project.
Number of Simulations: Specifies how many GBM paths to simulate, ensuring statistical relevance via the Central Limit Theorem (CLT).
Display Toggles:
Simulation Lines: Visual representation of individual GBM simulation paths.
Expected Value (EV) Line: The average price across all simulations at each projection bar.
Upper & Lower Confidence Bands: 95% confidence intervals indicating potential price boundaries.
EV of EV Line: Running average of EV values, providing a smoothed central tendency across the projection period. Additionally, this line often acts as an indicator of trend direction.
Visualization:
Clear and distinguishable lines with customizable colors and styles.
Overlayed on the price chart for direct comparison with actual price movements.
Mathematical Foundation
Geometric Brownian Motion (GBM):
Definition: GBM is a continuous-time stochastic process used to model stock prices. It assumes that the logarithm of the stock price follows a Brownian motion with drift.
Equation:
S(t)=S0⋅e(μ−12σ2)t+σW(t)
S(t)=S0⋅e(μ−21σ2)t+σW(t) Where:
S(t)S(t) = Stock price at time tt
S0S0 = Initial stock price
μμ = Drift coefficient (average return)
σσ = Volatility coefficient (standard deviation of returns)
W(t)W(t) = Wiener process (standard Brownian motion)
Drift (μμ) and Volatility (σσ):
Drift (μμ) represents the expected return of the stock.
Volatility (σσ) measures the stock's price fluctuation intensity.
Central Limit Theorem (CLT):
Principle: With a sufficiently large number of independent simulations, the distribution of the sample mean (EV) approaches a normal distribution, regardless of the underlying distribution.
Application: Ensures that the EV and confidence bands are statistically reliable.
Expected Value (EV) and Confidence Bands:
EV: The mean price across all simulations at each projection bar.
Confidence Bands: Range within which the actual price is expected to lie with a specified probability (e.g., 95%).
EV of EV (Mean of Sample Means):
Definition: Represents the running average of EV values across the projection period, offering a smoothed central tendency.
Methodology
Anchor Time Setup:
The indicator starts projecting from a user-defined Anchor Time. If not customized, it defaults to the current bar's timestamp.
Purpose: Allows users to analyze projections from a specific historical point or the latest market data.
Calculating Drift and Volatility:
Returns Calculation: Computes the logarithmic returns from the Anchor Time to the current bar.
returns=ln(StSt−1)
returns=ln(St−1St)
Drift (μμ): Calculated as the simple moving average (SMA) of returns over the period since the Anchor Time.
Volatility (σσ): Determined using the standard deviation (stdev) of returns over the same period.
Simulation Generation:
Number of Simulations: The user defines how many GBM paths to simulate (e.g., 30).
Projection Candles: Determines the number of future bars to project (e.g., 12).
Process:
For each simulation:
Start from the current close price.
For each projection bar:
Generate a random number zz from a standard normal distribution.
Calculate the next price using the GBM formula:
St+1=St⋅e(μ−12σ2)+σz
St+1=St⋅e(μ−21σ2)+σz
Store the projected price in an array.
Expected Value (EV) and Confidence Bands Calculation:
EV Path: At each projection bar, compute the mean of all simulated prices.
Variance and Standard Deviation: Calculate the variance and standard deviation of simulated prices to determine the confidence intervals.
Confidence Bands: Using the standard normal z-score (1.96 for 95% confidence), establish upper and lower bounds:
Upper Band=EV+z⋅σEV
Upper Band=EV+z⋅σEV
Lower Band=EV−z⋅σEV
Lower Band=EV−z⋅σEV
EV of EV (Running Average of EV Values):
Calculation: For each projection bar, compute the average of all EV[j] values up to that bar.
EV of EV[j]=1j+1∑k=0jEV[k]
EV of EV[j]=j+11k=0∑jEV[k]
Visualization: Plotted as a dynamic line reflecting the evolving average EV across the projection period.
Visualization Elements
Simulation Lines:
Appearance: Semi-transparent blue lines representing individual GBM simulation paths.
Purpose: Illustrate a range of possible future price trajectories based on current drift and volatility.
Expected Value (EV) Line:
Appearance: Solid orange line.
Purpose: Shows the average projected price at each future bar across all simulations.
Confidence Bands:
Upper Band: Dashed green line indicating the upper 95% confidence boundary.
Lower Band: Dashed red line indicating the lower 95% confidence boundary.
Purpose: Highlight the range within which the price is statistically expected to remain with 95% confidence.
EV of EV Line:
Appearance: Dashed purple line.
Purpose: Displays the running average of EV values, providing a smoothed trend of the central tendency across the projection period. As the mean of sample means it approximates the population mean (i.e. the trend since the anchor point.)
Current Price:
Appearance: Semi-transparent white line.
Purpose: Serves as a reference point for comparing actual price movements against projected paths.
Usage Instructions
Configuring User Inputs:
Anchor Time:
Set to a specific timestamp to start projections from a historical point or leave it as default to use the current bar's time.
Projection Candles (Bars):
Define the number of future bars to project (e.g., 12). Adjust based on your trading timeframe and analysis needs.
Number of Simulations:
Specify the number of GBM paths to simulate (e.g., 30). Higher numbers yield more accurate EV and confidence bands but may impact performance.
Display Toggles:
Show Simulation Lines: Toggle to display or hide individual GBM simulation paths.
Show Expected Value Line: Toggle to display or hide the EV path.
Show Upper Confidence Band: Toggle to display or hide the upper confidence boundary.
Show Lower Confidence Band: Toggle to display or hide the lower confidence boundary.
Show EV of EV Line: Toggle to display or hide the running average of EV values.
Managing TradingView's Object Limits:
Understanding Limits:
TradingView imposes a limit on the number of graphical objects (e.g., lines) that can be rendered. High values for projection candles and simulations can quickly consume these limits. TradingView appears to only allow a total of 55 candles to be projected, so if you want to see two complete lines, you would have to set the projection length to 27: since 27 * 2 = 54 and 54 < 55.
Optimizing Performance:
Use Toggles: Enable only the necessary visual elements. For instance, disable simulation lines and confidence bands when focusing on the EV and EV of EV lines. You can also use the maximum projection length of 55 with the lower limit confidence band as the only line, visualizing a long horizon for your risk.
Adjust Parameters: Lower the number of projection candles or simulations to stay within object limits without compromising essential insights.
Interpreting the Indicator:
Simulation Lines (Blue):
Represent individual potential future price paths based on GBM. A wider spread indicates higher volatility.
Expected Value (EV) Line (Goldenrod):
Shows the mean projected price at each future bar, providing a central trend.
Confidence Bands (Green & Red):
Indicate the statistical range (95% confidence) within which the price is expected to remain.
EV of EV Line (Dotted Line - Goldenrod):
Reflects the running average of EV values, offering a smoothed perspective of expected price trends over the projection period.
Current Price (White):
Serves as a benchmark for assessing how actual prices compare to projected paths.
Practical Applications
Risk Management:
Confidence Bands: Help in identifying potential support and resistance levels based on statistical confidence intervals.
EV Path: Assists in setting realistic target prices and stop-loss levels aligned with projected expectations.
Trend Analysis:
EV of EV Line: Offers a smoothed trendline, aiding in identifying overarching market directions amidst price volatility. Indicative of the population mean/overall trend of the data since your anchor point.
Scenario Planning:
Simulation Lines: Enable traders to visualize multiple potential outcomes, fostering better decision-making under uncertainty.
Performance Evaluation:
Comparing Actual vs. Projected Prices: Assess how actual price movements align with projected scenarios, refining trading strategies over time.
Mathematical and Statistical Insights
Simulation Integrity:
Independence: Each simulation path is generated independently, ensuring unbiased and diverse projections.
Randomness: Utilizes a Gaussian random number generator to introduce variability in diffusion terms, mimicking real market randomness.
Statistical Reliability:
Central Limit Theorem (CLT): By simulating a sufficient number of paths (e.g., 30), the sample mean (EV) converges to the population mean, ensuring reliable EV and confidence band calculations.
Variance Calculation: Accurate computation of variance from simulation data ensures precise confidence intervals.
Dynamic Projections:
Running Average (EV of EV): Provides a cumulative perspective, allowing traders to observe how the average expectation evolves as the projection progresses.
Customization and Enhancements
Adjustable Parameters:
Tailor the projection length and simulation count to match your trading style and analysis depth.
Visual Customization:
Modify line colors, styles, and transparency to enhance clarity and fit chart aesthetics.
Extended Statistical Metrics:
Future iterations can incorporate additional metrics like median projections, skewness, or alternative confidence intervals.
Dynamic Recalculation:
Implement logic to automatically update projections as new data becomes available, ensuring real-time relevance.
Performance Considerations
Object Count Management:
High simulation counts and extended projection periods can lead to a significant number of graphical objects, potentially slowing down chart performance.
Solution: Utilize display toggles effectively and optimize projection parameters to balance detail with performance.
Computational Efficiency:
The script employs efficient array handling and conditional plotting to minimize unnecessary computations and object creation.
Conclusion
The Anchored GBM Projections + EV & Confidence Bands indicator is a robust tool for traders seeking to forecast potential future price movements using statistical models. By integrating Geometric Brownian Motion simulations with expected value calculations and confidence intervals, it offers a comprehensive view of possible market scenarios. The addition of the "EV of EV" line further enhances analytical depth by providing a running average of expected values, aiding in trend identification and strategic decision-making.
Hope it helps!
Version: Pine Script v6
Overlay: Yes
Author: [Gary Sebastian Brown III]
Published On: [12-31-24]
Overview
The Anchored GBM Projections + EV & Confidence Bands indicator leverages the Geometric Brownian Motion (GBM) model to project future price movements based on historical data. By simulating multiple potential future price paths, it provides traders with insights into possible price trajectories, their expected values, and confidence intervals. Additionally, it offers a "Mean of EV" (EV of EV) line, representing the running average of expected values across the projection period.
Key Features
Anchor Time Setup:
Define a specific point in time from which the projections commence.
By default, it uses the current bar's timestamp but can be customized.
Projection Parameters:
Projection Candles (Bars): Determines the number of future bars (time periods) to project.
Number of Simulations: Specifies how many GBM paths to simulate, ensuring statistical relevance via the Central Limit Theorem (CLT).
Display Toggles:
Simulation Lines: Visual representation of individual GBM simulation paths.
Expected Value (EV) Line: The average price across all simulations at each projection bar.
Upper & Lower Confidence Bands: 95% confidence intervals indicating potential price boundaries.
EV of EV Line: Running average of EV values, providing a smoothed central tendency across the projection period. Additionally, this line often acts as an indicator of trend direction.
Visualization:
Clear and distinguishable lines with customizable colors and styles.
Overlayed on the price chart for direct comparison with actual price movements.
Mathematical Foundation
Geometric Brownian Motion (GBM):
Definition: GBM is a continuous-time stochastic process used to model stock prices. It assumes that the logarithm of the stock price follows a Brownian motion with drift.
Equation:
S(t)=S0⋅e(μ−12σ2)t+σW(t)
S(t)=S0⋅e(μ−21σ2)t+σW(t) Where:
S(t)S(t) = Stock price at time tt
S0S0 = Initial stock price
μμ = Drift coefficient (average return)
σσ = Volatility coefficient (standard deviation of returns)
W(t)W(t) = Wiener process (standard Brownian motion)
Drift (μμ) and Volatility (σσ):
Drift (μμ) represents the expected return of the stock.
Volatility (σσ) measures the stock's price fluctuation intensity.
Central Limit Theorem (CLT):
Principle: With a sufficiently large number of independent simulations, the distribution of the sample mean (EV) approaches a normal distribution, regardless of the underlying distribution.
Application: Ensures that the EV and confidence bands are statistically reliable.
Expected Value (EV) and Confidence Bands:
EV: The mean price across all simulations at each projection bar.
Confidence Bands: Range within which the actual price is expected to lie with a specified probability (e.g., 95%).
EV of EV (Mean of Sample Means):
Definition: Represents the running average of EV values across the projection period, offering a smoothed central tendency.
Methodology
Anchor Time Setup:
The indicator starts projecting from a user-defined Anchor Time. If not customized, it defaults to the current bar's timestamp.
Purpose: Allows users to analyze projections from a specific historical point or the latest market data.
Calculating Drift and Volatility:
Returns Calculation: Computes the logarithmic returns from the Anchor Time to the current bar.
returns=ln(StSt−1)
returns=ln(St−1St)
Drift (μμ): Calculated as the simple moving average (SMA) of returns over the period since the Anchor Time.
Volatility (σσ): Determined using the standard deviation (stdev) of returns over the same period.
Simulation Generation:
Number of Simulations: The user defines how many GBM paths to simulate (e.g., 30).
Projection Candles: Determines the number of future bars to project (e.g., 12).
Process:
For each simulation:
Start from the current close price.
For each projection bar:
Generate a random number zz from a standard normal distribution.
Calculate the next price using the GBM formula:
St+1=St⋅e(μ−12σ2)+σz
St+1=St⋅e(μ−21σ2)+σz
Store the projected price in an array.
Expected Value (EV) and Confidence Bands Calculation:
EV Path: At each projection bar, compute the mean of all simulated prices.
Variance and Standard Deviation: Calculate the variance and standard deviation of simulated prices to determine the confidence intervals.
Confidence Bands: Using the standard normal z-score (1.96 for 95% confidence), establish upper and lower bounds:
Upper Band=EV+z⋅σEV
Upper Band=EV+z⋅σEV
Lower Band=EV−z⋅σEV
Lower Band=EV−z⋅σEV
EV of EV (Running Average of EV Values):
Calculation: For each projection bar, compute the average of all EV[j] values up to that bar.
EV of EV[j]=1j+1∑k=0jEV[k]
EV of EV[j]=j+11k=0∑jEV[k]
Visualization: Plotted as a dynamic line reflecting the evolving average EV across the projection period.
Visualization Elements
Simulation Lines:
Appearance: Semi-transparent blue lines representing individual GBM simulation paths.
Purpose: Illustrate a range of possible future price trajectories based on current drift and volatility.
Expected Value (EV) Line:
Appearance: Solid orange line.
Purpose: Shows the average projected price at each future bar across all simulations.
Confidence Bands:
Upper Band: Dashed green line indicating the upper 95% confidence boundary.
Lower Band: Dashed red line indicating the lower 95% confidence boundary.
Purpose: Highlight the range within which the price is statistically expected to remain with 95% confidence.
EV of EV Line:
Appearance: Dashed purple line.
Purpose: Displays the running average of EV values, providing a smoothed trend of the central tendency across the projection period. As the mean of sample means it approximates the population mean (i.e. the trend since the anchor point.)
Current Price:
Appearance: Semi-transparent white line.
Purpose: Serves as a reference point for comparing actual price movements against projected paths.
Usage Instructions
Configuring User Inputs:
Anchor Time:
Set to a specific timestamp to start projections from a historical point or leave it as default to use the current bar's time.
Projection Candles (Bars):
Define the number of future bars to project (e.g., 12). Adjust based on your trading timeframe and analysis needs.
Number of Simulations:
Specify the number of GBM paths to simulate (e.g., 30). Higher numbers yield more accurate EV and confidence bands but may impact performance.
Display Toggles:
Show Simulation Lines: Toggle to display or hide individual GBM simulation paths.
Show Expected Value Line: Toggle to display or hide the EV path.
Show Upper Confidence Band: Toggle to display or hide the upper confidence boundary.
Show Lower Confidence Band: Toggle to display or hide the lower confidence boundary.
Show EV of EV Line: Toggle to display or hide the running average of EV values.
Managing TradingView's Object Limits:
Understanding Limits:
TradingView imposes a limit on the number of graphical objects (e.g., lines) that can be rendered. High values for projection candles and simulations can quickly consume these limits. TradingView appears to only allow a total of 55 candles to be projected, so if you want to see two complete lines, you would have to set the projection length to 27: since 27 * 2 = 54 and 54 < 55.
Optimizing Performance:
Use Toggles: Enable only the necessary visual elements. For instance, disable simulation lines and confidence bands when focusing on the EV and EV of EV lines. You can also use the maximum projection length of 55 with the lower limit confidence band as the only line, visualizing a long horizon for your risk.
Adjust Parameters: Lower the number of projection candles or simulations to stay within object limits without compromising essential insights.
Interpreting the Indicator:
Simulation Lines (Blue):
Represent individual potential future price paths based on GBM. A wider spread indicates higher volatility.
Expected Value (EV) Line (Goldenrod):
Shows the mean projected price at each future bar, providing a central trend.
Confidence Bands (Green & Red):
Indicate the statistical range (95% confidence) within which the price is expected to remain.
EV of EV Line (Dotted Line - Goldenrod):
Reflects the running average of EV values, offering a smoothed perspective of expected price trends over the projection period.
Current Price (White):
Serves as a benchmark for assessing how actual prices compare to projected paths.
Practical Applications
Risk Management:
Confidence Bands: Help in identifying potential support and resistance levels based on statistical confidence intervals.
EV Path: Assists in setting realistic target prices and stop-loss levels aligned with projected expectations.
Trend Analysis:
EV of EV Line: Offers a smoothed trendline, aiding in identifying overarching market directions amidst price volatility. Indicative of the population mean/overall trend of the data since your anchor point.
Scenario Planning:
Simulation Lines: Enable traders to visualize multiple potential outcomes, fostering better decision-making under uncertainty.
Performance Evaluation:
Comparing Actual vs. Projected Prices: Assess how actual price movements align with projected scenarios, refining trading strategies over time.
Mathematical and Statistical Insights
Simulation Integrity:
Independence: Each simulation path is generated independently, ensuring unbiased and diverse projections.
Randomness: Utilizes a Gaussian random number generator to introduce variability in diffusion terms, mimicking real market randomness.
Statistical Reliability:
Central Limit Theorem (CLT): By simulating a sufficient number of paths (e.g., 30), the sample mean (EV) converges to the population mean, ensuring reliable EV and confidence band calculations.
Variance Calculation: Accurate computation of variance from simulation data ensures precise confidence intervals.
Dynamic Projections:
Running Average (EV of EV): Provides a cumulative perspective, allowing traders to observe how the average expectation evolves as the projection progresses.
Customization and Enhancements
Adjustable Parameters:
Tailor the projection length and simulation count to match your trading style and analysis depth.
Visual Customization:
Modify line colors, styles, and transparency to enhance clarity and fit chart aesthetics.
Extended Statistical Metrics:
Future iterations can incorporate additional metrics like median projections, skewness, or alternative confidence intervals.
Dynamic Recalculation:
Implement logic to automatically update projections as new data becomes available, ensuring real-time relevance.
Performance Considerations
Object Count Management:
High simulation counts and extended projection periods can lead to a significant number of graphical objects, potentially slowing down chart performance.
Solution: Utilize display toggles effectively and optimize projection parameters to balance detail with performance.
Computational Efficiency:
The script employs efficient array handling and conditional plotting to minimize unnecessary computations and object creation.
Conclusion
The Anchored GBM Projections + EV & Confidence Bands indicator is a robust tool for traders seeking to forecast potential future price movements using statistical models. By integrating Geometric Brownian Motion simulations with expected value calculations and confidence intervals, it offers a comprehensive view of possible market scenarios. The addition of the "EV of EV" line further enhances analytical depth by providing a running average of expected values, aiding in trend identification and strategic decision-making.
Hope it helps!
Notas de Lançamento
Update Announcement: Anchored GBM Projections + EV & Confidence BandsWhat’s New?
Separate Anchors for Drift (μμ) and Volatility (σσ):
Drift and volatility are now independently anchored to their own datetime settings.
This allows for greater flexibility and precision in capturing different market dynamics.
Traders can align drift with long-term trends and volatility with shorter-term fluctuations.
Improved Flexibility and Customization:
Separate anchors ensure that each parameter reflects the most relevant data based on its specific behavior in the market.
This helps avoid conflicts, improves runtime performance, and aligns more closely with real-world financial theory.
Clearer Theoretical Basis:
This update incorporates a nuanced understanding of how drift and volatility behave in financial markets, ensuring that the indicator delivers meaningful and accurate projections.
Drift reflects long-term trend expectations, while volatility captures market uncertainty and risk.
Granular Control for Strategic Trading:
Traders can now use independent anchors to tailor projections to specific timeframes, events, or strategies.
This separation also enables more robust backtesting and optimization of trading strategies.
Why This Update Matters
More Accurate Projections:
By separating the anchors for drift and volatility, the indicator now provides a more granular and reliable representation of the price action.
Drift calculations are not influenced by short-term noise, and volatility updates adapt quickly to changes in market conditions.
Enhanced Risk Management:
Monitoring volatility independently allows traders to manage risk more effectively, as they can react to sudden changes in market sentiment without altering their trend-based strategies.
Alignment with Financial Theory:
Drift and volatility are distinct components in modeling asset prices, and this update reflects that reality by treating them independently.
This alignment ensures that the indicator remains relevant and theoretically sound.
Clarification on Use Cases
Drift (μμ):
Anchored to a specific datetime to capture the long-term trend.
Ideal for analyzing macroeconomic trends, sustained market movements, or historical growth patterns.
Volatility (σσ):
Anchored to a different datetime to reflect short-term risk and uncertainty.
Useful for assessing market reactions to news events, earnings announcements, or other high-impact factors.
What Stays the Same?
Core Methodology: The indicator continues to use Geometric Brownian Motion (GBM) for projections, integrating an Expected Value (EV) line, Confidence Bands, and Simulation Lines to provide a robust predictive framework.
User-Friendly Customization: Toggle the display of simulation lines, confidence bands, EV lines, or even the "Mean of EVs" for clearer analysis.
Projection Length and Number of Simulations: Easily adjustable to suit your trading preferences, with optimized defaults for clarity and performance.
Example Use Case
Scenario: A trader wants to analyze the effect of a geopolitical event on a trending asset.
Drift Anchor: Set to January 1, 2024, to capture the asset's long-term uptrend.
Volatility Anchor: Set to March 1, 2024, when the event caused a spike in volatility.
Result:
The drift reflects the continued upward trajectory of the asset price, while volatility adjusts to reflect the market's reaction to the geopolitical event, creating a more nuanced and actionable projection.
Notas de Lançamento
📢 Update Announcement: Anchored GBM Projections + EV & Adjustable Confidence Bands🚀 What’s New?
Adjustable Confidence Bands:
User-Defined Confidence Percentage: Traders can now input any confidence percentage (ranging from 1% to 99%) to customize the width of the confidence bands.
Default Set to 68%: The default confidence band is now set to 68%, mirroring the behavior of standard Bollinger Bands, which represent approximately one standard deviation from the mean.
Separate Anchors for Drift (μμ) and Volatility (σσ):
Independent DateTime Anchors: Drift and volatility calculations are each anchored to distinct datetime settings, allowing for more precise and independent analysis of market trends and volatility dynamics.
Enhanced User Experience:
Simplified Inputs: Users no longer need to input Z-scores directly. Instead, they can simply specify their desired confidence percentage, making the tool more intuitive and user-friendly.
Improved Risk Management: The ability to adjust confidence bands empowers traders to tailor the indicator to their specific risk management strategies, such as using a 50% confidence range for tighter risk controls.
🔍 Why This Update Matters
Greater Flexibility and Precision:
Tailored Confidence Levels: By allowing traders to set their own confidence percentages, the indicator becomes highly adaptable to various trading styles and risk appetites.
Alignment with Bollinger Bands: Setting the default to 68% aligns the confidence bands with one standard deviation, a widely recognized measure in technical analysis, enhancing the indicator’s compatibility with established trading strategies.
Enhanced Risk Management:
Customizable Risk Boundaries: Traders can now define narrower or wider confidence bands based on their risk tolerance, enabling more effective risk management and position sizing.
Dynamic Adaptation: The adjustable bands can respond to changing market conditions, providing real-time insights into potential price movements within the specified confidence range.
Improved Analytical Accuracy:
Independent Drift and Volatility Anchors: Separating the anchors for drift and volatility ensures that each parameter accurately reflects its respective market behavior without interference, leading to more reliable projections.
🛠 How to Use the New Features
Accessing the Updated Indicator:
Add to Chart: Locate the updated indicator in your TradingView account under "My Scripts" or search for its name in the Public Library if published.
Open Pine Editor: If you have the script saved locally, open it in the Pine Editor to review or make further adjustments.
Configuring Confidence Bands:
Default Setting: The confidence bands are set to 68% by default, representing approximately one standard deviation—similar to Bollinger Bands.
Adjusting the Percentage:
Navigate to the indicator’s settings by clicking the gear icon next to its name on the chart.
Locate the "Confidence Percentage" input field.
Input Desired Percentage: Enter any value between 1% and 99% to set your preferred confidence level.
Example: Enter 50 for a 50% confidence range or 95 for a 95% confidence range.
Understanding the Visualization:
Simulation Lines (Blue): Represent individual Geometric Brownian Motion (GBM) paths based on drift and volatility.
Expected Value (EV) Line (Orange): The average projected price across all simulations.
Confidence Bands (Green & Red): The upper and lower bounds based on the user-defined confidence percentage.
EV of EV Line (Orange Dashed): A running average of the EV values, providing a smoothed trend line.
Current Price (White): The latest price point for reference.
📈 Example Use Case
Scenario: A trader aims to manage risk more effectively by using a 50% confidence range instead of the traditional 95%.
Set Confidence Percentage:
Open the indicator settings.
Change "Confidence Percentage" from 68% to 50%.
Analyze the Chart:
Observe the narrower Green and Red confidence bands, representing a 50% confidence interval.
Use these bands to make more conservative trading decisions, such as tighter stop-loss placements.
Benefits:
Increased Precision: Tighter bands offer a clearer view of likely price movements within a shorter confidence range.
Enhanced Risk Control: Facilitates more stringent risk management strategies by focusing on a higher probability of staying within the defined range.
📌 What Stays the Same?
Core Methodology: The indicator continues to utilize Geometric Brownian Motion (GBM) for generating price projections, ensuring robust and theoretically sound forecasts.
User-Friendly Customization: All other customization options remain intact, allowing users to toggle simulation lines, EV lines, and more based on their preferences.
Projection Length and Number of Simulations: These parameters remain adjustable, enabling users to fine-tune the indicator’s performance according to their analytical needs.
🔧 Technical Adjustments in the Script
Confidence Percentage to Z-Score Conversion:
A single-line function (f_invNormal) approximates the inverse cumulative distribution function (CDF) to convert the user-inputted confidence percentage into the corresponding Z-score.
This ensures that confidence bands accurately reflect the desired probability range without requiring manual Z-score inputs.
Dynamic Confidence Bands:
Confidence bands are now dynamically calculated based on the user-defined confidence percentage, allowing for real-time adjustments and more responsive risk boundaries.
📝 Final Thoughts
This update enhances the Anchored GBM Projections + EV & Confidence Bands indicator by introducing adjustable confidence bands, empowering traders to tailor their risk management strategies with greater precision. By setting the default confidence to 68%, the indicator now offers a familiar and practical standard similar to Bollinger Bands, while also providing the flexibility to customize based on individual trading preferences.
Notas de Lançamento
Fixed a runtime error issue. Also cleaned up the terribly messy chart pic from before. Notas de Lançamento
Release Note: Anchored GBM with Skew/Kurt Damping vX.XThis update to the Anchored GBM indicator introduces significant enhancements, including the incorporation of skewness and kurtosis adjustments, providing more robust and realistic forward projections that better reflect market behavior.
Key Features:
Skewness & Kurtosis Integration:
The indicator now calculates skewness and kurtosis based on anchored returns, allowing it to account for asymmetry and fat-tail behavior in the price distribution.
Damped Random Draw Adjustments:
Random draws in the simulation are adjusted using the calculated skewness and kurtosis values, modified by user-configurable damping factors. This adjustment ensures that the simulations reflect realistic tail behavior while preventing over-amplification of extremes:
zadjusted=z+skew×skew_damp3.0 z2+(kurt−3.0)×kurt_damp24.0 z3
zadjusted=z+3.0skew×skew_dampz2+24.0(kurt−3.0)×kurt_dampz3
Fully Anchored Calculations:
Drift, volatility, skewness, and kurtosis are calculated from fixed anchor points, providing stability and ensuring that projections are less affected by short-term fluctuations.
Customizable Inputs:
The update introduces user-defined anchor times for drift, volatility, skewness, and kurtosis, along with damping factors for skewness and kurtosis. This allows fine-tuning to match specific trading scenarios.
Comprehensive Visualization:
The indicator includes projection paths, expected value (EV) lines, and upper/lower confidence bands, offering clear visual insights into possible future price ranges.
Benefits:
The addition of skewness and kurtosis adjustments makes the Anchored GBM indicator a more powerful tool for traders and analysts. By capturing and incorporating the asymmetric and fat-tailed nature of market data, the indicator now provides more realistic simulations of price movements, making it ideal for analyzing risk and uncertainty.
This release represents a significant step forward in creating realistic and flexible market simulations, enhancing its value for quantitative analysis and trading.
Script de código aberto
Em verdadeiro espírito do TradingView, o criador deste script o tornou de código aberto, para que os traders possam revisar e verificar sua funcionalidade. Parabéns ao autor! Embora você possa usá-lo gratuitamente, lembre-se de que a republicação do código está sujeita às nossas Regras da Casa.
Aviso legal
As informações e publicações não se destinam a ser, e não constituem, conselhos ou recomendações financeiras, de investimento, comerciais ou de outro tipo fornecidos ou endossados pela TradingView. Leia mais nos Termos de Uso.
Script de código aberto
Em verdadeiro espírito do TradingView, o criador deste script o tornou de código aberto, para que os traders possam revisar e verificar sua funcionalidade. Parabéns ao autor! Embora você possa usá-lo gratuitamente, lembre-se de que a republicação do código está sujeita às nossas Regras da Casa.
Aviso legal
As informações e publicações não se destinam a ser, e não constituem, conselhos ou recomendações financeiras, de investimento, comerciais ou de outro tipo fornecidos ou endossados pela TradingView. Leia mais nos Termos de Uso.